FDA and ISO 13485 Compliance Requirements for Auto-Injector Component Moulding
Auto-injectors represent a critical class of combination products, integrating complex mechanical actuation systems with primary drug containment components. The functional integrity and dimensional precision of moulded components are pivotal to the performance and reliability of these devices. Accordingly, the component manufacturing process — particularly injection moulding — must operate within a tightly controlled and validated framework to comply with global regulatory standards, chiefly 21 CFR Part 820 (FDA Quality System Regulation) and ISO 13485:2016.
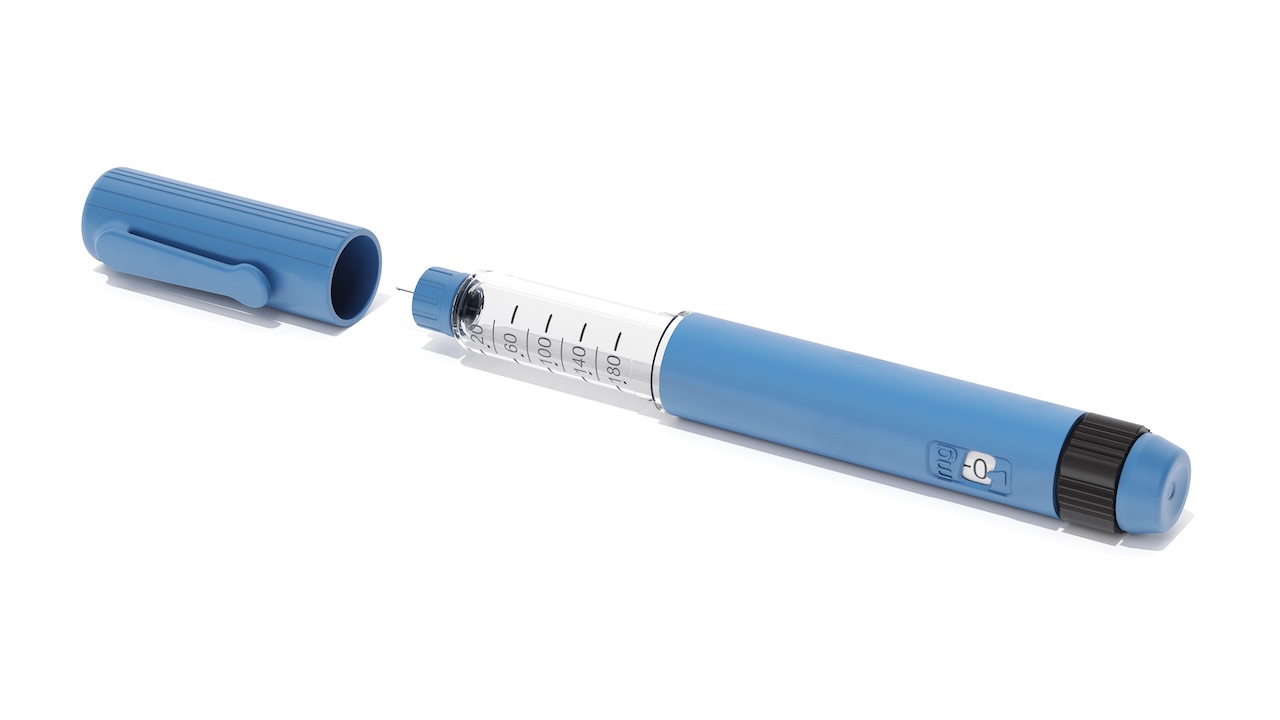
Design Transfer and Component Specification Control
Under both ISO 13485 §7.3 and FDA 21 CFR §820.30 (Design Controls), design transfer requires the translation of design outputs into manufacturing specifications. For moulded auto-injector components, this includes:
- Detailed 2D and 3D CAD drawings with GD&T annotations.
- Material specifications (e.g. ISO 10993-1 biocompatibility requirements, USP <661.1>/<661.2> polymer compliance).
- Dimensional tolerances in microns (especially for snap fits, spring cavities, or plunger interfaces).
- Surface finish criteria (e.g. Ra value limits for mating surfaces or sliding interfaces).
Design Verification and Design Validation (DV/DV) must confirm that parts produced via moulding meet critical-to-function (CTF) characteristics, especially for components involved in drug containment (e.g. needle shrouds, cartridge sleeves) or mechanical actuation (e.g. torsion springs, drive mechanisms).
Supplier Qualification and Material Lot Traceability
Injection moulding is often outsourced, making supplier quality assurance essential. ISO 13485 §7.4 and FDA §820.50 require:
- Supplier risk classification based on the component’s impact on patient safety and product functionality.
- Execution of supplier audits to ISO 13485 or IATF 16949 (automotive-grade moulders).
- Establishment of incoming inspection protocols including first article inspection (FAI) and statistical sampling (ANSI Z1.4 or ISO 2859).
Materials (e.g. PEEK, PC, COP/COC, PA12) must be fully traceable to lot and batch level. Certificates of Analysis (CoA) and compliance with REACH, RoHS, and extractables/leachables standards must be available for every lot used.
Process Validation: IQ/OQ/PQ Methodology
Process validation is a core regulatory requirement under ISO 13485 §7.5.6 and FDA §820.75. Given the narrow tolerance windows typical of drug delivery components, robust validation is non-negotiable. The standard validation lifecycle includes:
- Installation Qualification (IQ): Verifying machine installation, utilities (e.g. chiller temp stability ±1°C), and tooling compatibility.
- Operational Qualification (OQ): Establishing process windows for critical parameters — barrel temperature, injection pressure, hold time, cooling time. DOE (Design of Experiments) is commonly employed to define safe operating ranges.
- Performance Qualification (PQ): Producing a minimum of three full production runs under standard conditions, assessing dimensional and functional attributes across statistically significant sample sizes.
Attribute data (pass/fail) and variable data (e.g. critical dimension Cpk ≥ 1.33) must be statistically justified. All results must be documented in a Validation Master Plan (VMP) and individual validation protocols.
Environmental and Contamination Control
Cleanliness is particularly important for primary packaging components and parts in contact with the drug product. Though ISO Class 8 is common for auto-injector component manufacturing, higher cleanliness levels (ISO Class 7 or better) may be required based on risk assessment and intended use.
Controls include:
- Environmental monitoring (particle counts per ISO 14644-1 and microbial levels per ISO 14698).
- Tooling cleaning and validation – ensuring no residual lubricants, plasticisers, or degradation byproducts.
- Anti-static controls – for charged polymers such as cyclic olefin polymers which can attract particulates.
Manufacturers must document all cleanroom classification and maintenance under an Environmental Control Plan as part of their quality management system (QMS).
Change Control and Risk-Based Approach
Any post-validation changes to tooling geometry, resin formulation, processing parameters, or secondary operations (e.g. degating, ultrasonic welding) require formal change control procedures under ISO 13485 §4.1.4 and FDA §820.30(i). All changes must be:
- Evaluated through Design Risk Analysis (e.g. PFMEA or DFMEA).
- Subject to re-validation when critical process parameters (CPPs) are impacted.
- Reviewed by a Change Control Board (CCB) with cross-functional representation.
ISO 14971:2019-compliant risk management files must be maintained, linking process risks to mitigations such as in-process controls, statistical process control (SPC), or increased sampling plans.
Ongoing Monitoring and Continuous Improvement
To maintain compliance, manufacturers must implement a robust post-validation monitoring system, which includes:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) for high-risk dimensions.
- Periodic requalification of moulding equipment (typically annually).
- Nonconformance trending and CAPA (Corrective and Preventive Action) systems per FDA §820.100 and ISO 13485 §8.5.
Where applicable, the use of Industry 4.0 technologies such as real-time cavity pressure sensors, automated vision inspection, and closed-loop process controls is increasingly encouraged to reduce variation and improve traceability.
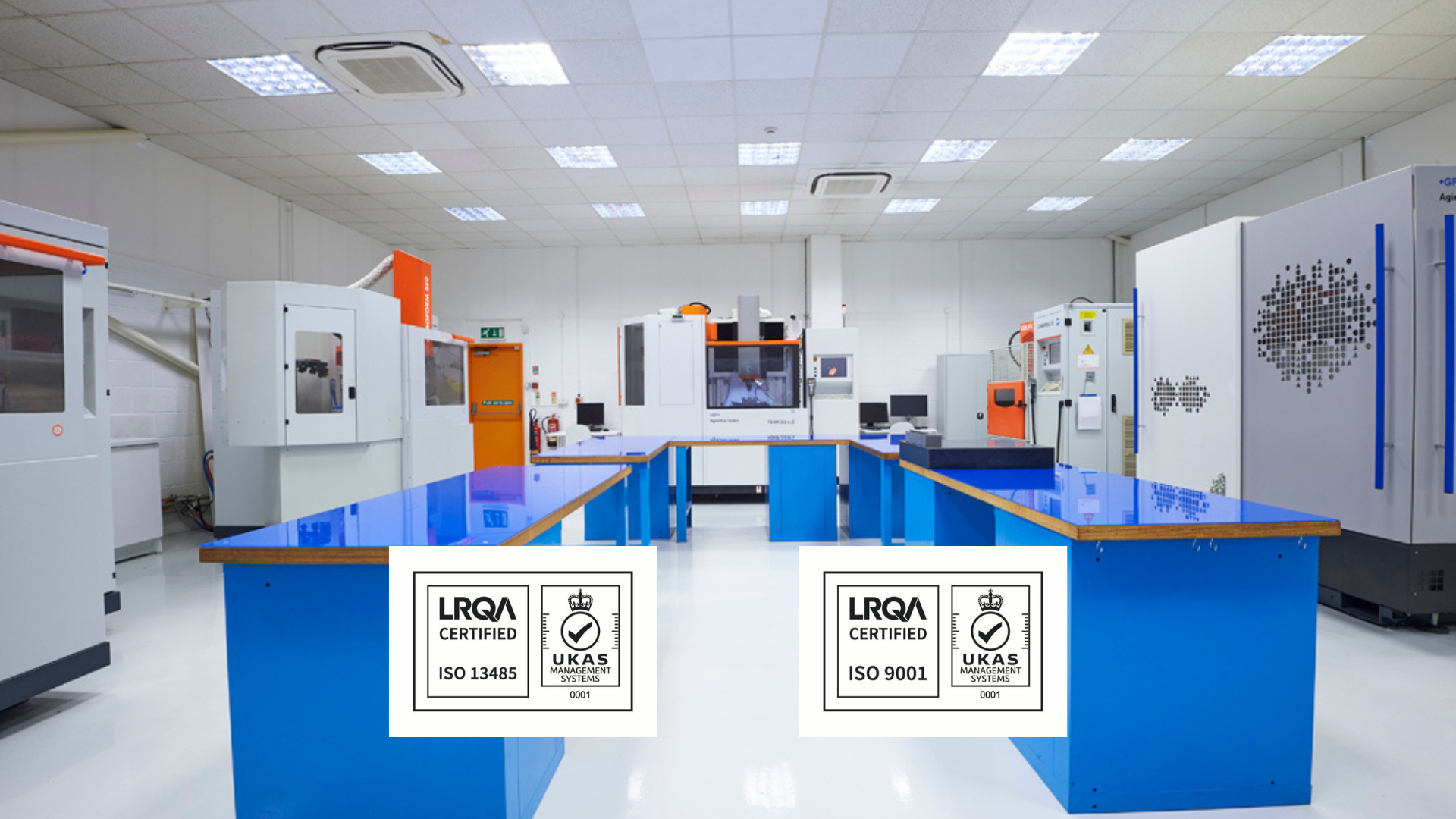

World-class facilities at Micro Systems
Partnering with Micro Systems offers medical device manufacturers a strategic advantage in the development and production of precision-moulded components for auto-injectors and drug delivery systems. With ISO 13485 and ISO 9001-certified facilities and deep expertise in micro moulding, high-precision tooling, and process validation, Micro Systems delivers exceptional part accuracy and repeatability — essential for meeting stringent FDA and international regulatory requirements. Their end-to-end support, from design for manufacturability (DFM) to validated production, ensures robust compliance and accelerated time to market for critical combination products.
Contact us today!




