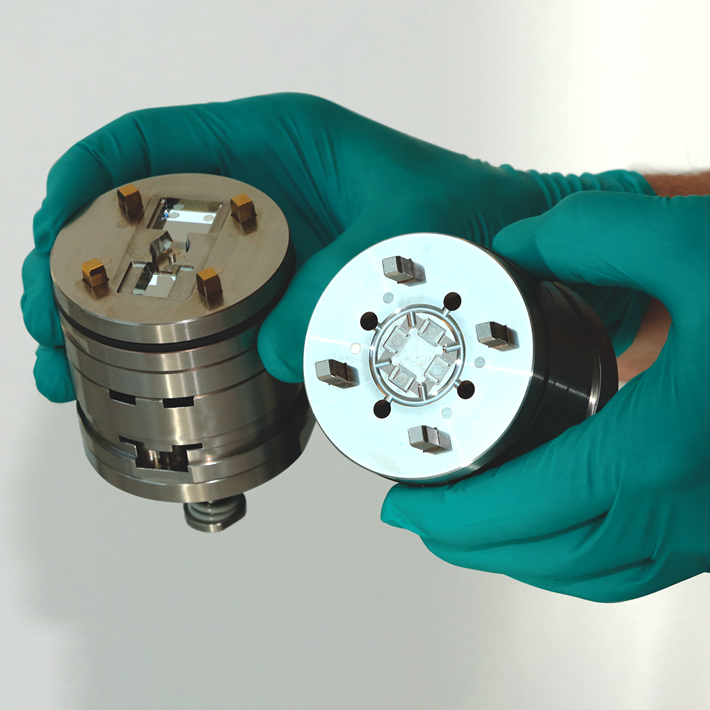
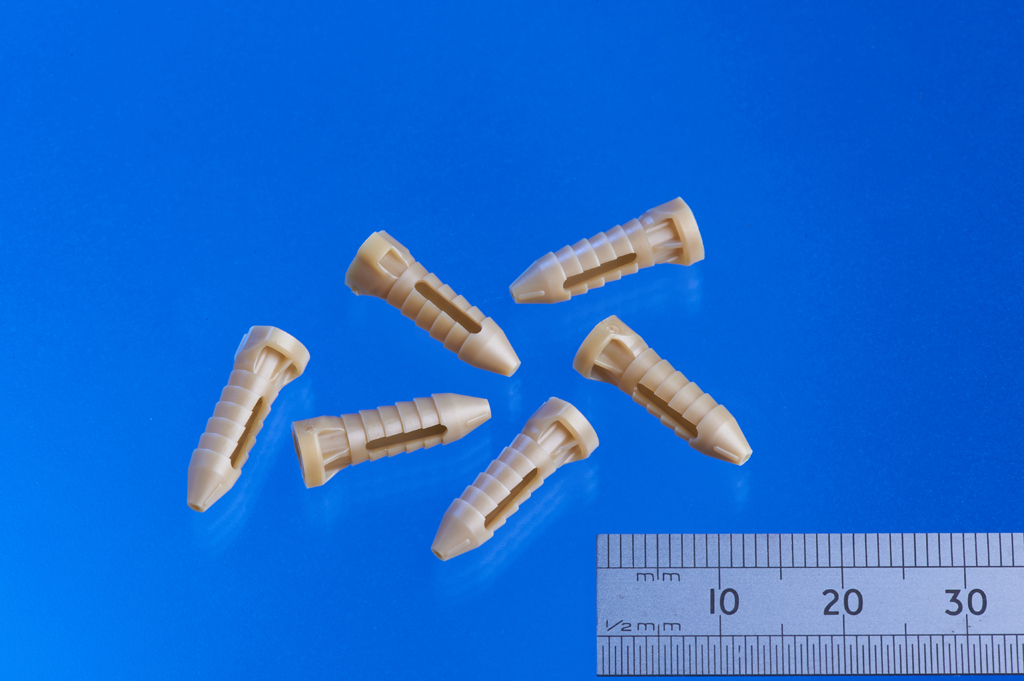
What is Medical Grade Plastic?
The modern healthcare system cannot function without products made of medical grade plastic. These materials are particularly designed and produced for use in medical products and devices, while meeting high international regulatory standards.

PEEK BONE IMPLANT replacing Titanium one (Photo: Micro Systems)
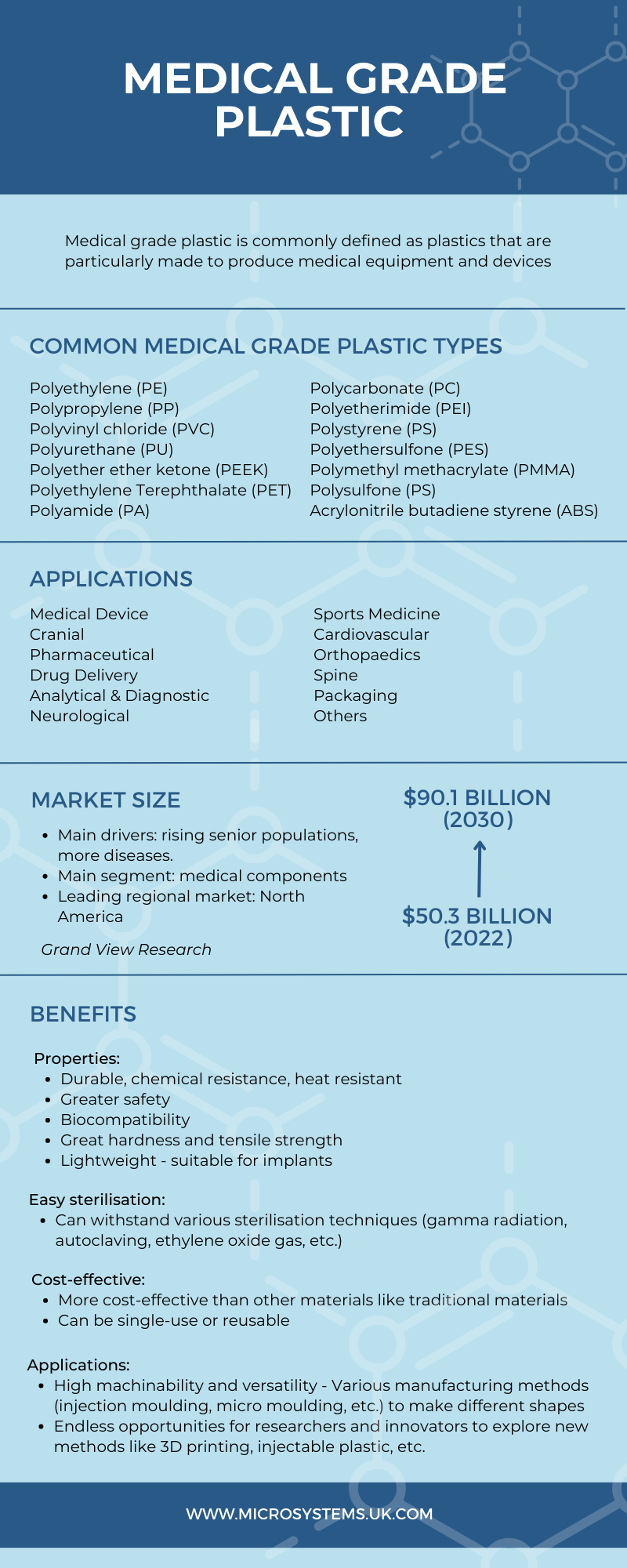
Medical Grade Plastic definition
Medical grade plastic refers to plastics specifically designed for medical devices, with biocompatible materials used to promote healing and minimise adverse reactions such as injuries, allergies, or toxicity.
These plastics are widely used in applications such as prosthetics, syringes, diagnostic tools, and pharmaceutical packaging. Polymers, derived from oil or petroleum, are favoured in medical device manufacturing due to their mouldability, superior chemical resistance, and lightweight nature—up to ten times lighter than metals.
What does it mean by medical grade?
A polymer’s biocompatibility must be rigorously tested before it can be deemed medical grade. The gold standard for biocompatibility testing protocols is described in the ISO 10993 standard, which is the greatest illustration of what a medical grade material is. While ISO 10993 only addresses biocompatibility, it also emphasises both the material and how the material is treated during manufacture.
ISO 10993 categorised medical devices according to the anticipated length of contact (length of use and length of being in touch with biological tissues) as follows:
- Class A devices: designed for brief exposure, i.e., up to 24 hours.
- Class B devices: designed for prolonged exposure, meaning they will probably come into contact with the body for longer than 24 hours but less than 30 days.
- Class C devices: designed to be in touch for an extended period of time (more than 30 days).
Key properties that make Medical Grade Plastic suitable for the industry:
- Plastic polymers can prevent the growth of bacteria and other disease-causing organisms because they are impermeable or non-permeable
- Plastic polymers can work with various manufacturing processes to be shaped into many different shapes
- Plastic polymers can be sterilised thanks to their resilience to heat and chemicals
- Plastic polymers have the ability to withstand wear thanks to their hardness
- Plastic polymers’ biocompatibility guarantees that they won’t lead to harmful or immunological responses.
The market for Medical Grade Plastic
According to a research by Grand View Research, the global medical plastics market was valued at USD 50.3 billion in 2022 and is projected to grow at a CAGR of 7.7% from 2023 to 2030, reaching USD 90.1 billion. Growth drivers include the ageing population in North America, Europe, and Asia, as well as the rising incidence of various diseases.
In 2022, the medical components segment led the market with over 40% share, followed by mobility aids, medical packaging, sterilisation, implants, orthopaedic goods, and biopharmaceutical devices. North America was the leading region, accounting for over 33% of total sales.
Types of Medical Grade Plastic
There are many different kinds of plastic polymers used for medical purposes, but thermoplastics are the ones that are most frequently used for medical injection moulding. Plastic polymers known as thermoplastics soften when heated and stiffen when cooled. The following are some of the thermoplastics used most frequently in medical injection moulding:
Polypropylene (PP):
Semi-crystalline thermoplastic polypropylene (PP) is produced through the catalytic polymerisation of propene. Recognised for its high quality in medical applications, polypropylene offers excellent purity, low water absorption, superior chemical resistance, dimensional stability, machinability, and resistance to steam autoclaving. Special medical-grade polypropylene can also be heat-stabilised for use at higher temperatures.
Applications: Orthopaedics, Medical Device, Spine, Sports Medicine, Drug Delivery, Pharmaceutical, Cardiovascular, Analytical & Diagnostic, Neurological.
Polyethylene (PE):
Polyethylene (PE) polymers are semi-crystalline thermoplastics known for their toughness, excellent chemical resistance, high impact strength, superior wear resistance, and exceptional low-temperature performance.
Applications: Pharmaceutical, Sports Medicine, Cardiovascular, Orthopedics, Medical Device, Drug Delivery, Analytical & Diagnostic.
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA):
Polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) is a high-grade plastic used in medical implants and equipment, such as intraocular lenses, bone cement, and cranial implants, due to its impact strength, chemical resistance, biocompatibility, and clarity.
Applications: Medical Device, Cranial, Pharmaceutical, Drug Delivery, Analytical & Diagnostic, Neurological.
Polycarbonates (PC):
Polycarbonate (PC) is an amorphous thermoplastic known for its high electrical properties, exceptional impact strength, toughness, and mild chemical resistance. Its transparency, due to low crystallinity, makes it ideal for medical-grade sheets, rods, and tubes that meet strict healthcare standards.
Applications: Drug Delivery, Pharmaceutical, Medical Device, Analytical & Diagnostic.
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK):
PEEK is a semi-crystalline engineering thermoplastic known for its excellent dimensional stability, chemical compatibility, biocompatibility, and electrical insulation. It is easy to machine and produces lighter, stronger, and more durable components for demanding conditions.
Applications: Neurological, Spine, Cranial, Orthopedics, Medical Device, Pharmaceutical, Drug Delivery, Cardiovascular, Analytical & Diagnostic.
Other commonly used Medical Grade Plastics include Acetal Copolymer (POM-C), Polysulfone (PSU), Polyphenylene Sulfide (PPS), etc.
Benefits of Medical Grade Plastic
Properties:
- Durable, chemical resistance, heat resistant
- Greater safety: non-permeable and shatter-proof so suitable for transporting biohazard materials or to prevent the spread of high-risk pathogens
- Biocompatibility: designed to be compatible with the human body to avoid negative responses.
- Some polymers have great hardness and tensile strength, for example, Nylon (2400 psi), PPS (12500 psi), PEEK (14000 psi), Ultem (15200 psi)
- Recyclable
- Lightweight – suitable for implants
Easy sterilisation:
- Can withstand various sterilisation techniques (gamma radiation, autoclaving, ethylene oxide gas, etc.)
Cost-effective:
- More cost-effective than other materials like metal, ceramics, glass, etc. thanks to lower material cost and lower manufacturing cost of large-scale production
- Can be single-use or reusable
Applications:
- High machinability and versatility – Various manufacturing methods (injection moulding, micro moulding, etc.) can be used to make different shapes
- Endless opportunities for researchers and innovators to explore new methods like 3D printing, injectable plastic, etc.
To achieve optimal results for your medical device and component projects, the team of experts at Micro Systems will collaborate with you from the outset, ensuring that the selected medical-grade plastic is the most suitable choice for both high performance and long-term cost-effectiveness.
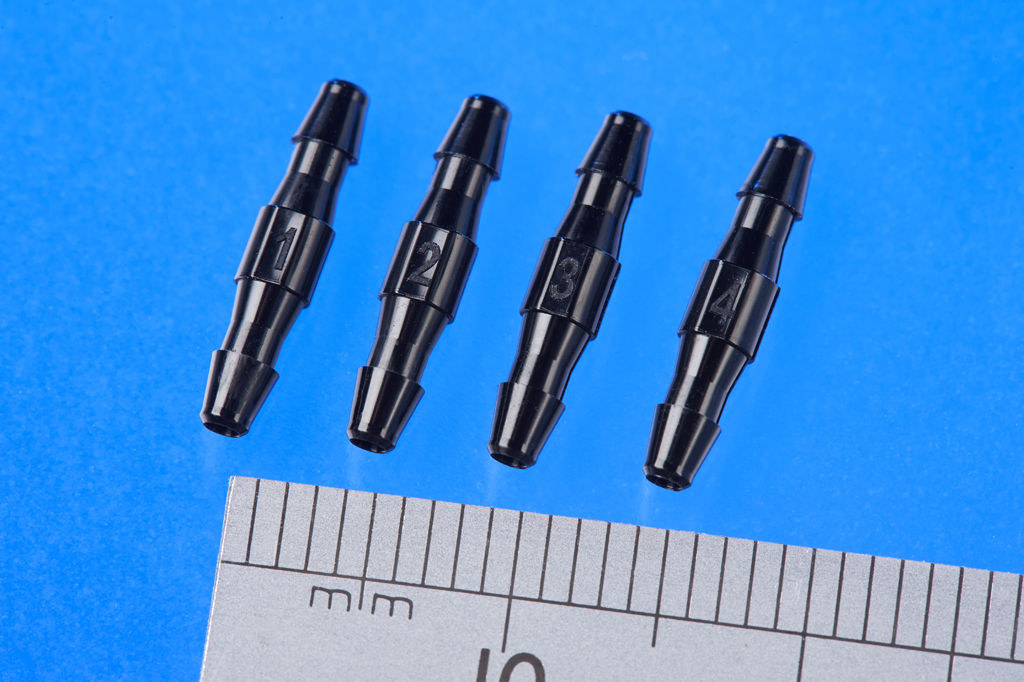

Micro Systems specialises in the design, manufacture and validation of ultra precision micro moulds for the medical, pharmaceutical and optical markets, at the same time, the development and use of micro and nano technologies in the design and manufacture of injection moulded components. We have a dedicated micro moulding facility, and have ISO13485 and ISO9001 certifications, and an ISO Class 7 Cleanroom. For more information, please Contact us or visit our website.