Top 5 Micro Injection Moulding Machines for Medical Applications in 2025
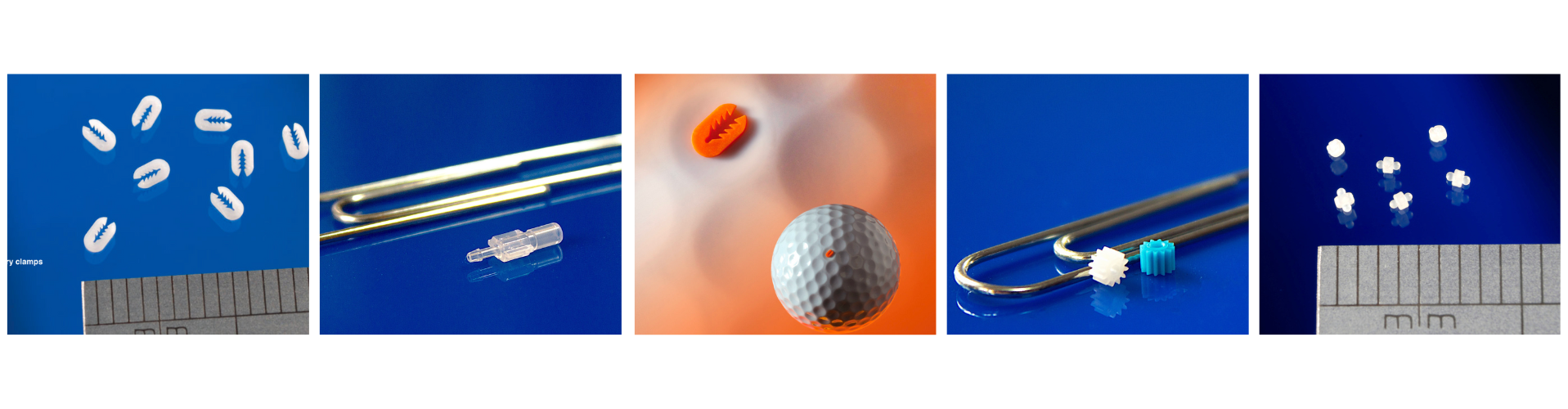
Micro injection moulding is at the forefront of medical device manufacturing—delivering minute, high-precision parts for diagnostics, drug delivery systems, microfluidics and minimally invasive tools. Find below the most advanced Micro Injection Moulding Machines for Medical Applications in 2025.
1. Wittmann Battenfeld MicroPower 15/10
Shot volumes: 0.05–4 cm³ via two-step screw‑and‑plunger design.
Precision: Sub‑0.1 g part weights; ±10–100 µm tolerances.
Clean‑room readiness: Fully enclosed cell accepts laminar‑flow module producing ISO 14644–1 Class 6 air; encapsulated drives are easy to clean. Envisaged as turnkey clean‑room production cell with integrated robot, rotary table and inspection camera (source).
Cost‑efficiency: Shorter cycle times and low energy/material waste can reduce costs by 30–50 % vs standard machines—critical when using materials at €2,000–5,000 / kg (source).
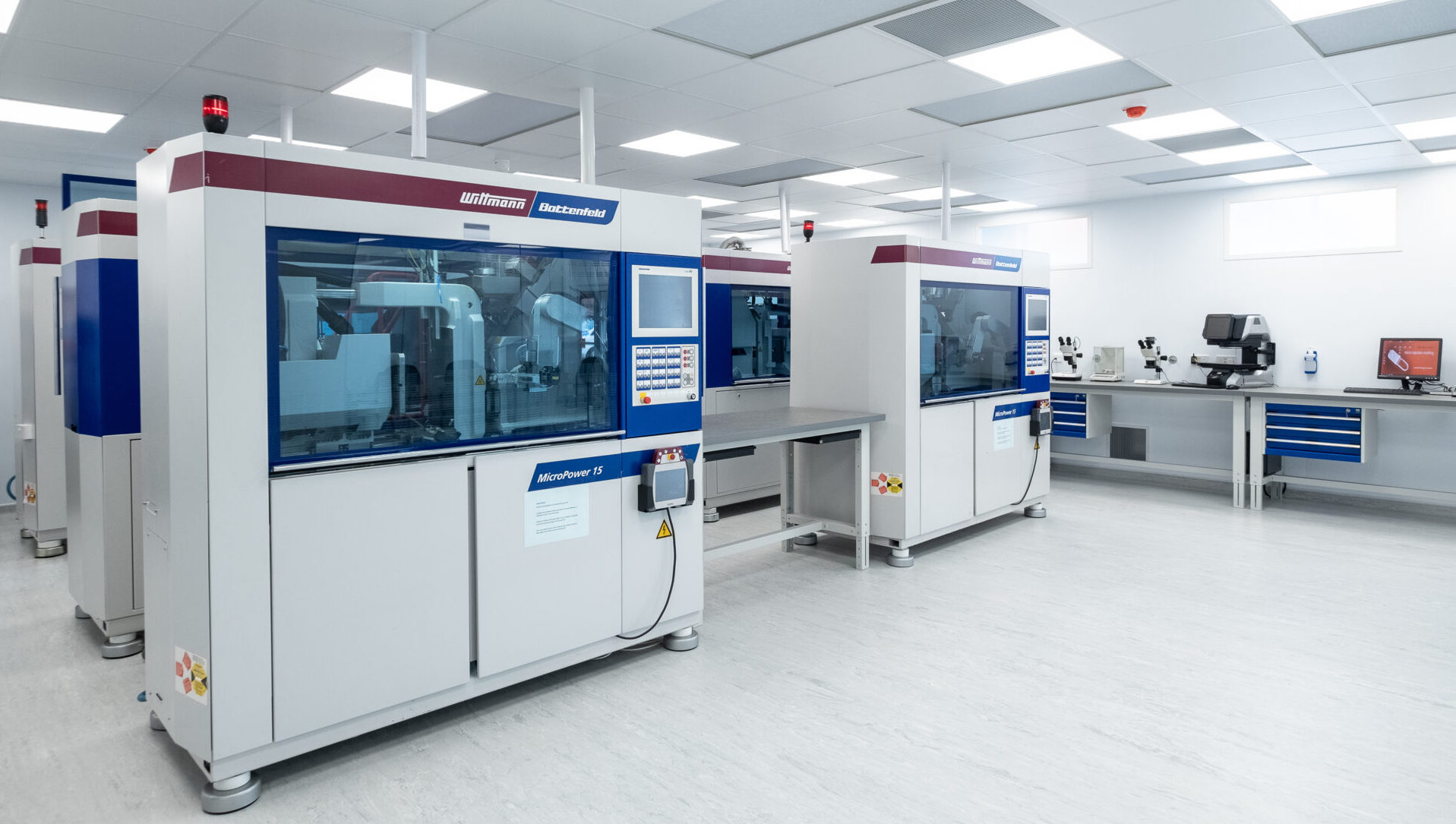

Top-of-the-field Wittmann Battenfeld MicroPower at Micro Systems
2. Fanuc Roboshot α‑S15iB
Performance: High‑precision all‑electric system ideal for optical‑grade parts and microfluidics.
Sustainability: Energy regeneration and servo‑driven efficiency cut power use by ~50 % versus hydraulics (source)
Application niche: Excellent for lab‑on‑chip and micro‑optics where shot consistency is paramount.
ROBOSHOT 𝛼-S15𝑖B machine (source: Fanuc Europe)
3. Sumitomo (SHI) Demag SE30DUZ / IntElect
Capability: Clamping forces around 150 kN; shot weights down to single-digit milligram range; able to produce parts like a 0.775 mm POM gear (source).
Automation: Compact size and integration with inline robotics yields efficient clean‑room cells.

IntElect (source: Sumitomo)
4. Engel e‑motion / e‑victory 50/30 TL (Tie‑bar‑free)
LSR Micro‑injection: Prototype systems are producing silicone lens elements in shot sizes as low as 0.0005 g (source).
Footprint: Tie‑bar‑free design enhances mould access and space efficiency in cramped clean‑room environments.
Process integration: At NPE, Engel demoed one‑step drip‑chamber production (moulding, filter insertion, overmoulding) inside a clean‑room cell (source).
)
Engel e‑motion / e‑victory 50/30 TL (source: Engel)
5. Arburg Allrounder (Micro version)
Injection precision: ±0.1 % repeatability, up to 2,500 bar pressure—ideal for microfluidics & multi‑material components (source).
Automation: SELOGICA control supports plug‑and‑play robotics within clean‑room‑ready platform.
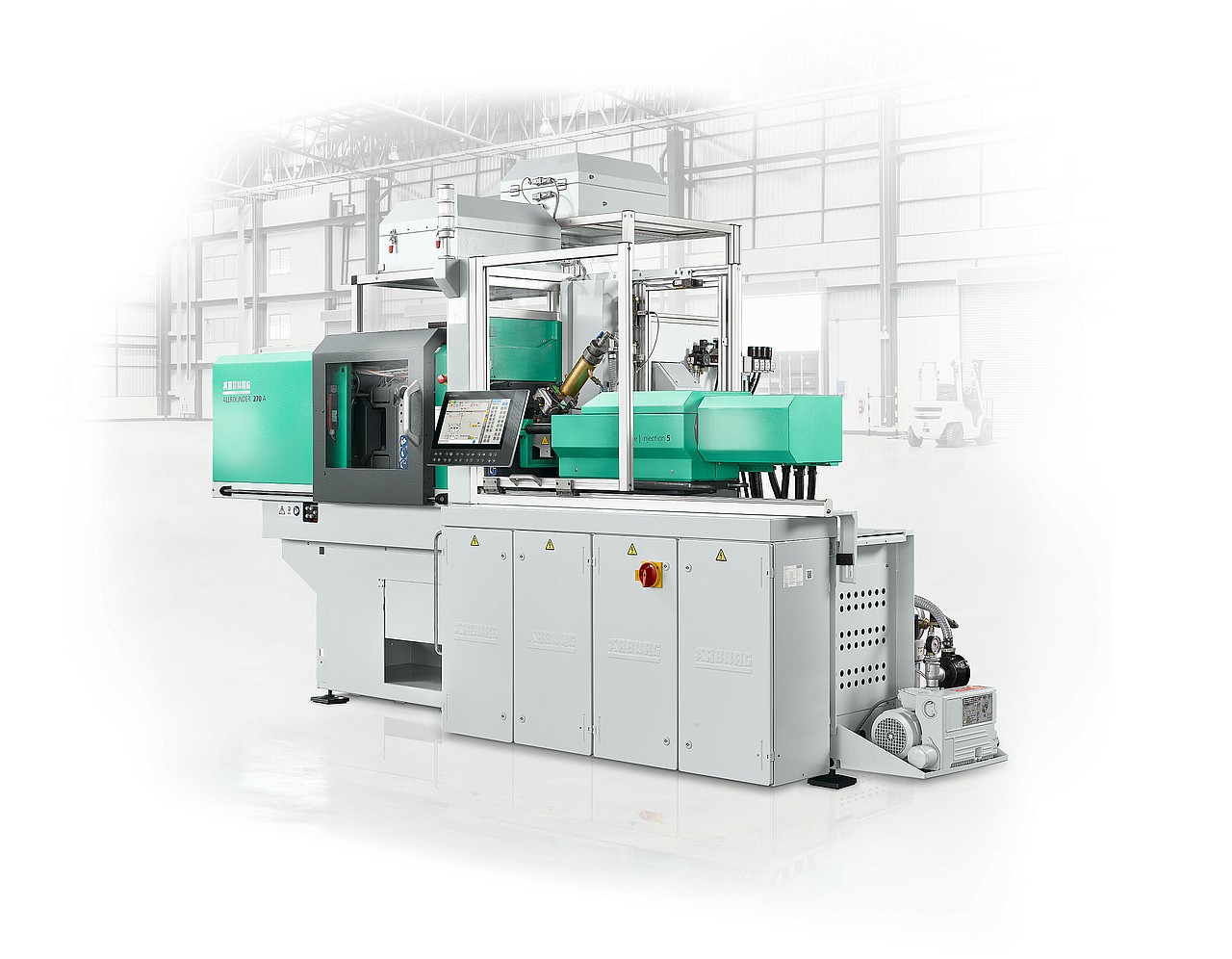

Arburg Allrounder (Micro version) (source: Arburg)
Clean‑Room Implementation Considerations for Micro Injection Moulding Machines
Air Purity Standards
ISO 14644-1 Class 6 laminar-flow environments have become the benchmark for producing micro-scale medical components, ensuring controlled airborne particle levels.
Hygienic Machine Architecture
Design features such as enclosed drive systems, smooth external surfaces, and sealed machine housings facilitate thorough cleaning and significantly reduce particulate contamination.
Optimised Space Utilisation
Tie-bar-free configurations (as seen in Engel machines) and modular, compact manufacturing cells (such as those from Wittmann) maximise floor space efficiency—especially valuable where clean-room expansion is impractical or cost-restrictive.
Built-In Quality Control
Integrated vision systems and robotic handling within the production cell support continuous in-line inspection, maintaining sterility while enabling 100% part validation without external intervention.
Cost‑Analysis & ROI Breakdown of Micro Injection Moulding Machines
| Cost Element | MicroPower 15/10 (All‑electric cell) | Standard Micro‑moulder |
| Machine cost | Higher upfront (electric drives & enclosure) | Lower (hydraulic or open-frame) |
| Energy consumption | ↓30–50 % (servo drives, reused regen power) | Baseline energy use |
| Material waste | ≪1 g sprue; micro gauges save €2k–5k/kg resin | Higher sprue weight; more waste |
| Labour & maintenance | Lower—automated removal/ inspection reduces staff | Requires manual inspection |
| Real-estate / CapEx | High density cells yield more parts per m² | More floor space per machine |
| Throughput | Fast cycles (~3–5 s), inline QC minimises downtime | Slower cycles, more manual steps |
Return on Investmen: Savings from material efficiency and energy alone can offset premium machine costs in under 12–18 months. Coupled with space‑efficiency in expensive clean‑room real estate and reduced labour, the ROI timeframe improves in high‑mix, low‑volume medical part production.
In 2025, micro injection moulding machines for medical applications share four key characteristics:
- Fine-control of shot volume and tolerance
- All-electric operation for energy, cleanliness, uptime
- Clean‑room compatibility via cell design and robotics
- Cost-efficiency from reduced waste, faster cycles, and integrated quality assurance
Choosing the right machine depends on:
- Required shot size and tolerance
- Handling of specialised materials (e.g., LSR, PEEK)
- Available clean‑room space and layout constraints
- Desired automation level and ROI timeline

With more than 20 years of experiences, along with the most advanced technologies in micro injection moulding, Micro Systems can provide a turnkey moulding solutions for your Medical Device projects.
Contact us today!