Understanding ISO 13485 Requirements in Medical Moulding
In the precision-driven world of medical device component manufacturing, adherence to ISO 13485:2016 is a critical requirement. For companies specialising in medical-grade plastic injection moulding, the standard provides the regulatory and operational framework necessary to manufacture products that meet stringent international regulatory requirements, particularly for use in Class II and Class III medical devices.
ISO 13485: A Manufacturing-Centric Overview
ISO 13485:2016 is the globally recognised Quality Management System (QMS) standard for organisations involved in the design, production, installation, and servicing of medical devices and related components. It aligns closely with regulatory frameworks such as the UK MDR, EU MDR 2017/745, and the US FDA 21 CFR Part 820.
For medical moulding facilities, it governs the end-to-end production lifecycle—from raw material control through to post-moulding processing, cleanroom packaging, and final product release.
Key ISO 13485 Requirements in Medical Moulding
1. Quality Management System (QMS) Structure
Medical moulding operations must implement a documented QMS that integrates seamlessly into production and quality control workflows. This includes:
- SOPs and WI for machine setup, tool changeovers, and in-process inspections
- Controlled documentation (e.g. revision control of mould validation protocols)
- Device Master Records (DMR) and Device History Records (DHR)
- Defined quality objectives, including CpK and PpK targets for critical dimensions
2. Process Validation (IQ/OQ/PQ)
All critical moulding processes must be validated to demonstrate process repeatability and capability under production conditions. This includes:
- IQ – Installation Qualification: verifying tooling, auxiliary equipment, and press setup
- OQ – Operational Qualification: establishing process parameter windows (e.g. melt temp, hold pressure, cycle time)
- PQ – Performance Qualification: confirming the process produces conforming parts over multiple lots under routine conditions
Validation must be backed by statistical analysis, including GR&R, DOE, and control charting.
3. Cleanroom Moulding & Environmental Monitoring
Where applicable, production must be carried out in certified ISO 14644-1 cleanrooms, typically Class 7 or Class 8, with:
- HEPA filtration and positive pressure differentials
- Validated environmental monitoring (particulates, microbial load)
- Personnel gowning protocols, training, and access control
- Routine cleanroom requalification per ISO 13485 and ISO 14698
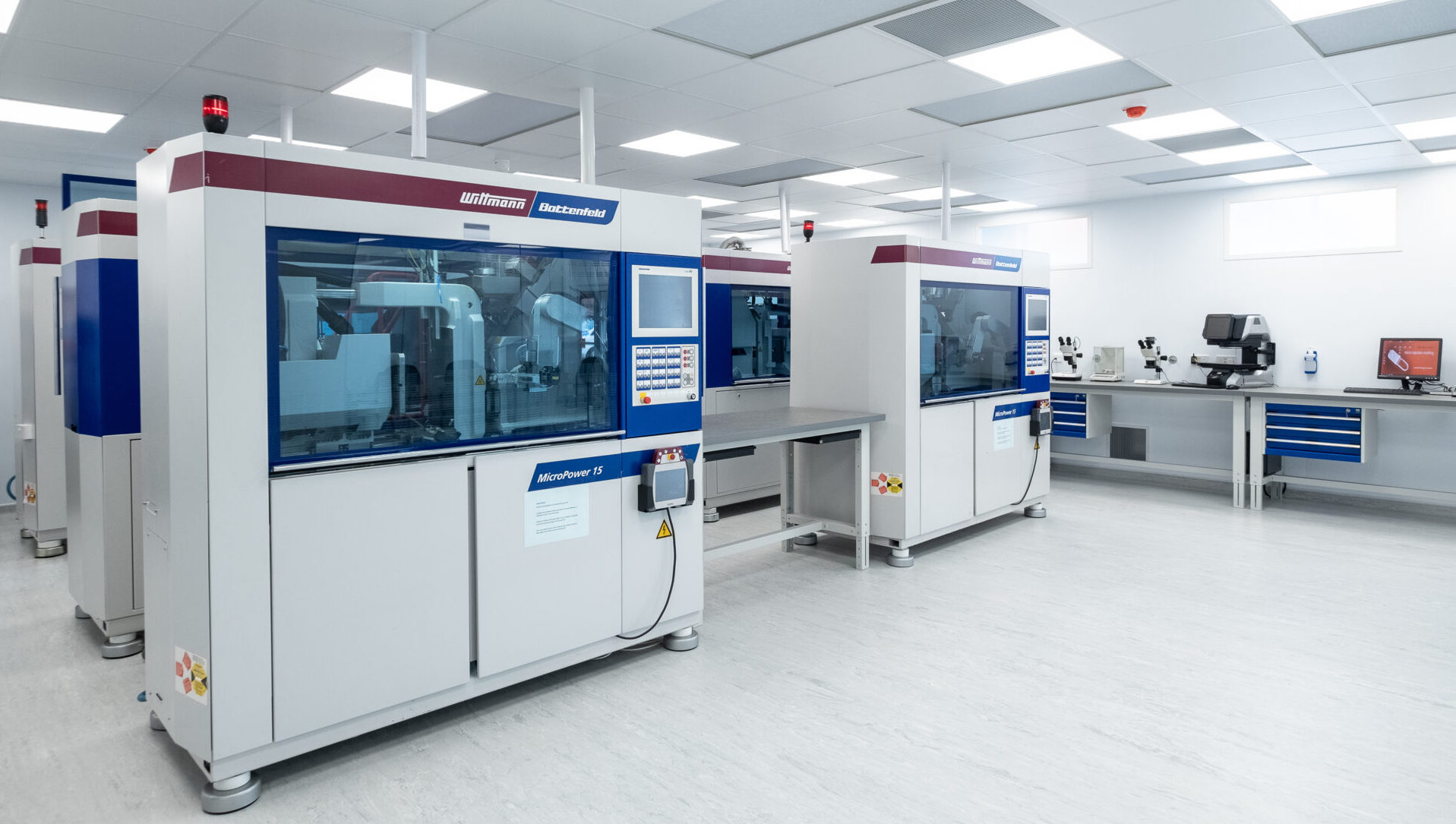

Clean room micro-moulding facilities at Micro Systems
4. Material Control and Traceability
Medical-grade polymers (e.g. PC, PEEK, LSR, TPU) must be sourced from certified suppliers and tracked via unique lot numbers through each stage:
- Raw material incoming inspection and certificate of analysis (COA) verification
- Lot-level traceability through blending, drying, and barrel loading
- Resin moisture content checks, especially for hygroscopic materials (e.g. Nylon, PETG)
- Full batch-level traceability to enable field recall if required
5. Product Realisation & Design Transfer
Where design-for-manufacture (DFM) input is provided, moulders must document and control the design transfer process, ensuring:
- Alignment of 2D/3D CAD models with mould design and tool steel selection
- Verification of critical-to-quality (CTQ) dimensions via CMM or vision inspection
- Use of scientific moulding principles during process development
- Cross-functional DFMEA reviews with customer engineering teams
6. Inspection, SPC, and In-Process Control
Real-time process monitoring and quality control are essential to meeting ISO 13485 expectations. Typical controls include:
- In-line visual inspection and automated vision systems
- SPC on critical dimensions using digital callipers, micrometres, or CMM
- First Article Inspection (FAI) and periodic requalification runs
- Attribute and variable data collection for trend analysis and CAPA triggers
7. Non-Conformance & CAPA Management
ISO 13485 requires robust non-conformance tracking and Corrective and Preventive Action (CAPA) workflows. Key practices include:
- Root cause investigation using 5 Whys, Fishbone/Ishikawa, or 8D methodology
- Documentation of disposition (e.g. scrap, rework, quarantine)
- Implementation of corrective actions via engineering change orders (ECOs)
- Trending of non-conformances for management review inputs
Integration with Regulatory and Customer Requirements
ISO 13485 is often required by OEMs as part of supplier qualification. Many medical moulding suppliers must also align with:
- FDA QSR requirements (21 CFR Part 820)
- EU MDR 2017/745 for CE marking
- UKCA and MHRA regulations
- OEM-specific supplier quality agreements (SQAs) and audits
Operational Benefits of ISO 13485 in Medical Moulding
Implementing ISO 13485 across a medical injection moulding operation provides significant strategic and operational advantages:
- Improved First Pass Yield (FPY) and reduced scrap
- Enhanced audit readiness for FDA, MHRA, or notified bodies
- Strengthened supplier confidence and long-term contracts with medical OEMs
- Data-driven process optimisation through trend monitoring
- Qualification for high-risk (Class III) medical device component manufacturing
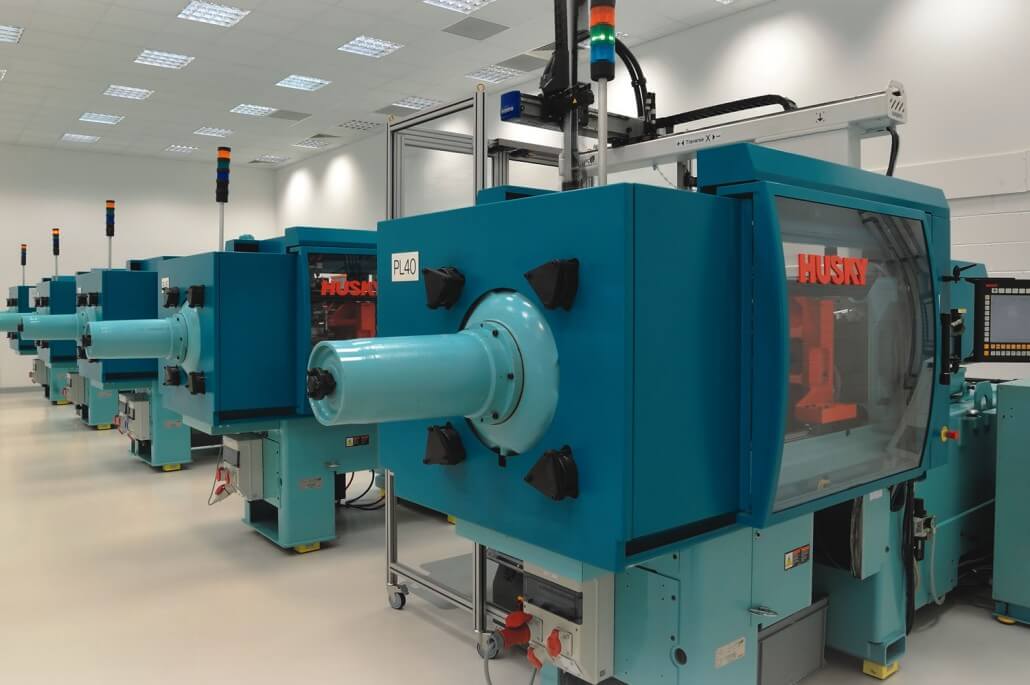

Moulding machines at Optimold, on-site injection moulding facility of Micro Systems
Why ISO 13485 Certification Is Difficult in Medical Moulding
Gaining ISO 13485 certification in the field of medical injection moulding is a demanding process due to the high standards of traceability, validation, and regulatory compliance required. Key challenges include:
- Process Validation: All moulding processes must be fully validated (IQ/OQ/PQ) with supporting statistical analysis such as CpK and GR&R.
- Traceability: Full lot-level traceability of materials, tooling, process parameters, and inspection data is mandatory.
- Cleanroom Requirements: Manufacturing must often occur in ISO Class 7 or 8 cleanrooms, with strict environmental and contamination controls.
- Documentation Load: A comprehensive QMS must be maintained with audit-ready records, SOPs, CAPAs, and risk files.
- Multi-Jurisdictional Compliance: Companies must align with global standards including FDA QSR, EU MDR, and UKCA in addition to ISO 13485.
These factors require significant investment in quality infrastructure, engineering resources, and ongoing audit readiness—making ISO 13485 one of the most challenging certifications in manufacturing.
 Micro Systems is ISO 13485 and ISO 9001 accredited, ensuring the highest standards for your medical moulding projects.
Micro Systems is ISO 13485 and ISO 9001 accredited, ensuring the highest standards for your medical moulding projects.
For medical moulding manufacturers, ISO 13485 is more than a compliance exercise—it is a systematic approach to risk-based manufacturing, document control, and process assurance. By embedding ISO 13485 principles into daily operations, manufacturers can produce high-precision medical components that meet the most rigorous global standards for quality and safety.
Whether you’re moulding single-use devices, surgical components, or implantable-grade plastics, ISO 13485 provides the foundation for repeatable, auditable, and scalable production. Micro Systems is ISO 13485 and ISO 9001 accredited, ensuring the highest standards for your medical moulding projects.