PEEK for medical uses
What is medical grade PEEK?
PEEK (polyether ether ketone) is a colourless organic thermoplastic polymer that belongs to the polyaryletherketone (PAEK) family. As a semicrystalline thermoplastic, PEEK retains its exceptional mechanical properties and resistance to high temperatures and chemicals. Due to its outstanding performance characteristics and biocompatibility, Medical Grade PEEK is increasingly recognised as a high-performance material in the medical sector.
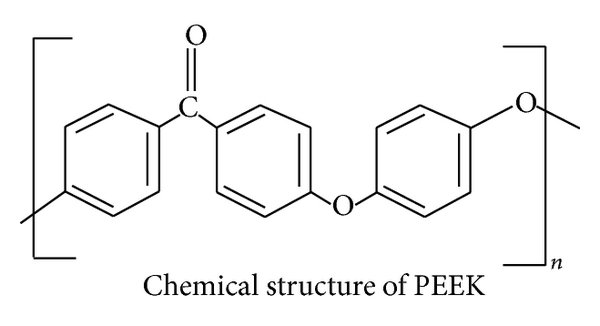
Source: Nanomodified Peek Dental Implants (1)
The history of PEEK
PEEK was first developed in 1978 for use in the aerospace industry. Its versatility quickly led to its adoption across various sectors, including pharmaceuticals, chemicals, food and beverage, aerospace, and healthcare. By the late 1990s, PEEK had become a viable alternative to metal implants, and in April 1998, it was promoted as a biomaterial for implants, initially applied in orthopaedic procedures, particularly spinal surgery. In 1999, Invibio Biomaterial Solutions developed PEEK-OPTIMA, the first implantable unfilled PEEK polymer. In 2007, image-contrast grades and carbon fibre-reinforced variations, offering significantly improved strength and stiffness, were introduced. Over the past two decades, PEEK has gained widespread clinical acceptance and has been used in a variety of medical applications, including cardiovascular and dental implants.
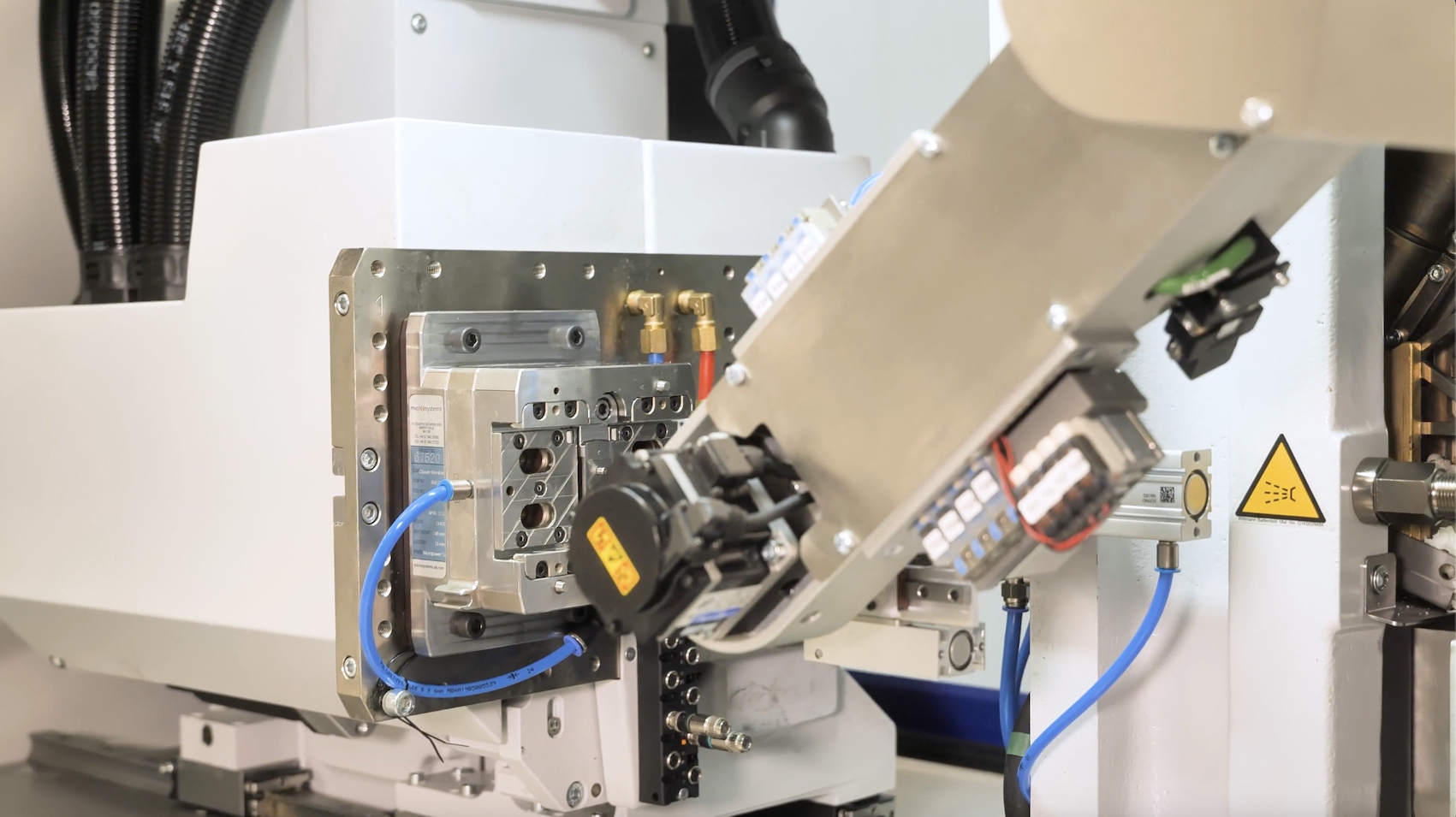
Photo: Micro Systems
What are the advantages of medical grade PEEK ?
PEEK is one of the few high-performance polymers classified as a biomaterial, distinguished by its exceptional mechanical, thermal, and chemical properties. These attributes, combined with its excellent radiation resistance and ease of sterilisation, make PEEK an ideal material for medical applications.
Biocompatibility: Due to its biocompatibility and established status as a validated biomaterial, PEEK is considered safe for use in in vivo applications. It exhibits no cytotoxic, genotoxic, or immunogenic effects. With over 20 years of successful use, PEEK has proven to be suitable for long-term applications in the medical field.
Modulus of elasticity like bone: PEEK is substantially more flexible than metals like titanium, stainless steel, and other metal biomaterials. It bends and supports weight in a way that is considerably more similar to bone, hence minimising stress shielding and encouraging the growth of bone.
Radiolucency: PEEK’s pure radiolucency makes it simple for surgical teams to monitor the location of implants and spot issues on X-rays, CT, and MRI scans.
Lower infection risk: PEEK’s hydrophobic properties and minimal surface roughness prevent bacterial adherence and infection risk.
Aesthetic features: PEEK implants are a fantastic option for a more aesthetically pleasing look because of its composite structure, elastic module, osteogenic capabilities, adequate fatigue limits, and other useful qualities.
 Other advantages of PEEK to be used for medical purposes include high strength and stiffness (Young’s modulus of elasticity of 3.6 GPa, tensile strength of 170 MPa), high heat resistance (343 °C – 662 °F), light weight, good chemical resistance and outstanding wear and abrasion resistance.
Other advantages of PEEK to be used for medical purposes include high strength and stiffness (Young’s modulus of elasticity of 3.6 GPa, tensile strength of 170 MPa), high heat resistance (343 °C – 662 °F), light weight, good chemical resistance and outstanding wear and abrasion resistance.
What are the disadvantages of PEEK ?
PEEK is generally more expensive than other thermoplastics, which can make large-volume applications less cost-effective. Due to its high melting point of approximately 343°C, PEEK can be challenging to process, often requiring specialised tools and techniques, such as injection moulding equipment capable of operating at elevated temperatures. This can lead to a more complex and costly manufacturing process. Additionally, the limited availability of PEEK materials may further drive up production costs. PEEK also offers a limited range of colour options, typically in natural light brown or black. While PEEK has low resistance to UV light, this can be improved by incorporating a carbon additive into the material formulation.

Photo: Micro Systems
The applications of PEEK in Healthcare
Orthopaedic implants
PEEK is commonly used in orthopaedic implants, including trauma fixation plates, joint replacements, knee and hip arthroplasty, and spinal fusion cages. Its mechanical properties closely resemble those of bone, making it an ideal material for load-bearing applications, ensuring it can support weight and move in a similar manner to bone. Additionally, PEEK’s radiolucency allows orthopaedic teams to monitor the body’s response after partial or total joint replacement. Due to its biocompatibility, PEEK integrates effectively with surrounding tissue. Furthermore, PEEK is significantly lighter than metal, allowing patients to adjust joints and limbs with less effort compared to using heavier metal alternatives.
Dental implants
PEEK is widely used in dental applications, including detachable partial dentures, dental implants, temporary crowns and bridges, braces, and surgical equipment for the oral cavity. One of its most notable features is its superior abrasion and compression resistance, which enables it to withstand the mechanical stresses of chewing and biting. The radiolucency of PEEK is particularly beneficial for dental practitioners, providing enhanced diagnostic capabilities and offering patients improved comfort and aesthetics. PEEK dental implants are well-regarded for their ability to closely resemble natural teeth (especially tooth-coloured variants), maintaining taste sensation, ensuring comfort, and being less likely to cause allergic reactions or irritation.
Spinal applications
PEEK has been widely used as a material for spinal implants for many years and remains a leading choice in spinal surgery. Its continued application, along with ongoing advancements, suggests it may become the preferred option for a broader range of patients. PEEK is highly favoured for spinal implant procedures due to its radiolucency and optimal modulus, which closely mimics that of cortical bone. This modulus ensures the implant bears weight in a manner similar to native bone, reducing the risk of subsidence and preventing density loss in adjacent bone. Its radiolucency also allows surgeons to monitor the healing process and implant integration post-surgery. Both of these critical properties can be tailored for specific clinical needs. For example, barium sulphate can be added to PEEK to enhance contrast for surgeons who require reduced radiolucency. Common spinal applications of PEEK include minimally invasive spinal implants, interspinous spacers, posterior spine stabilisation rods, and anterior cervical plates.
Other medical device non-implant applications
PEEK is widely used for the housing and structural components of various medical devices, including electronic devices, portable surgical instruments, and monitoring equipment, due to its mechanical strength, resistance to sterilisation, and biocompatibility. Additionally, PEEK is commonly found in medical pumps, pistons, fluid transfer systems, and valves. It is also well-established in critical medical and pharmaceutical applications, such as dialysis equipment, blood pumps, infusion pumps, reusable medical instruments, medical device fixtures, and tissue cutting tools, where PEEK seals and bearings provide reliable performance.
Injection Moulding of PEEK
With its properties, PEEK is suitable for the production of ultra-precision (micro) plastic parts with tight tolerance using injection moulding method. When using injection moulding for PEEK, several key considerations must be addressed to achieve a successful outcome. PEEK resin requires heating to very high temperatures, typically at or above the upper range of most injection moulding machines. Given the high sensitivity of PEEK to anisotropic shrinkage during cooling, it is essential to apply the correct pressure to the mould to maintain product integrity. Additionally, it is crucial to ensure that PEEK is properly cured before moulding, which involves eliminating any residual moisture through a controlled and monitored system to ensure accurate part dimensions. For medical applications, the entire production process must be conducted in a clean, temperature-controlled environment, as any contamination could render the moulded parts unsuitable for end use. Larger gates are also recommended in PEEK injection moulding, as PEEK exhibits higher shrinkage compared to other amorphous thermoplastics, improving efficiency and part quality.
At Micro Systems, we have years of experience working with PEEK, in both Mould Manufacture and Injection Moulding. Our moulded PEEK medical parts can achieve the smallest size and tolerance that you require. Contact us today to discuss your PEEK medical parts!
(1). Nanomodified Peek Dental Implants: Bioactive Composites and Surface Modification—A Review – Scientific Figure on ResearchGate. Available from: https://www.researchgate.net/figure/The-chemical-structural-formula-of-polyetheretherketone-PEEK-PEEK-is-a-semicrystalline_fig1_279842270 [accessed 25 Sep, 2023]